There are a fair number of private and public forecasters with whom I speak that anticipate a significant market decline in March. As you know I tend to agree to some extent, but with the important caveat that we are in a very different monetary landscape than the last time the Fed engaged in quantitative easing, the early 1930's. In short, I may allow for it, but I am not doing anything different about it -- yet.
The biggest difference is the lack of external standards. This introduces an element of policy decision that has been discussed here on several occasions. In other words, the Fed retains the option, albeit with increasing difficulty, to create another bubble, and levitate stock market prices in the face of deteriorating economic fundamentals.
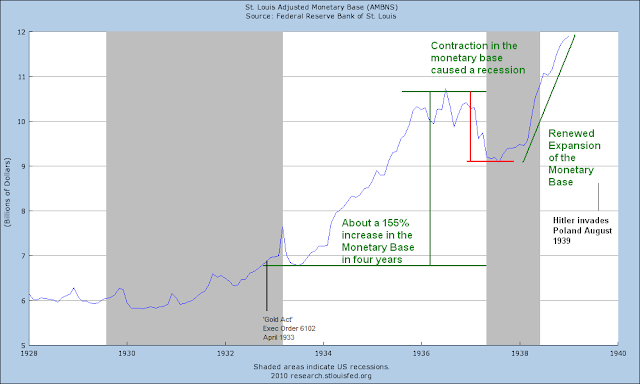
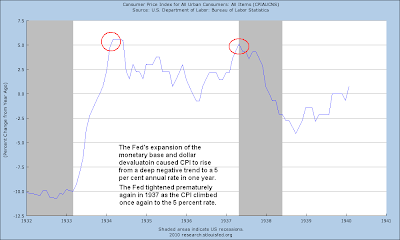
The dollar was formally devalued by around 40% in 1933. We may yet see that done this time, but more gradually and informally. This is what makes gold controversial today; it exposes the financial engineering. So they feel the need to manage it, to denigrate it as an alternative to their paper. They want to have their cake, and eat it too.
Let's review where we are today.
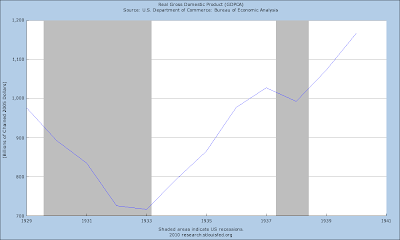
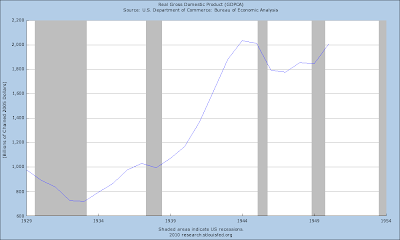
The Bear Market of 2007-2009, marked by the Crash of 2008, has been a massive decline in equity prices precipitated by the bursting of the credit bubble centered around housing prices and packaged debt obligations of highly questionable valuations. The cause of the bubble was easy Fed monetary policy and the loosened regulation of the financial sector, which reopened the door to old frauds with new names.
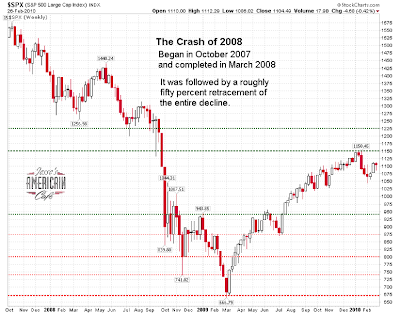
Even today, I think most people do not appreciate the sheer magnitude of the decline, and the damage it has done to the real economy. This is the result, I believe, of three factors:
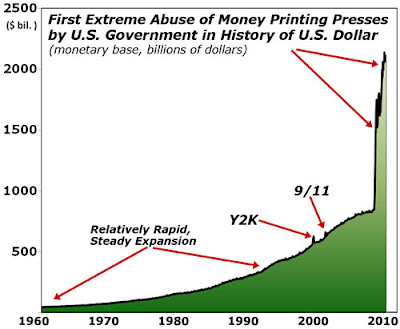
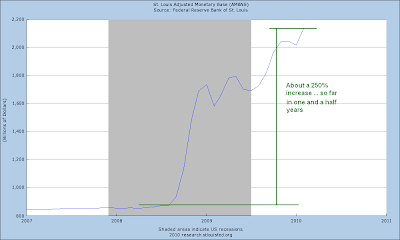
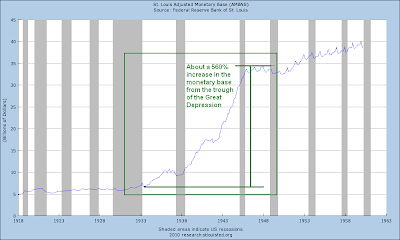
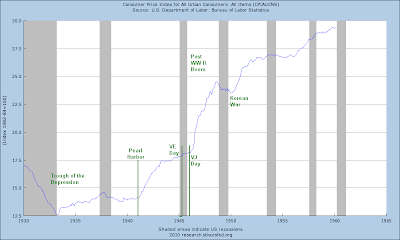
1. An extraordinary expansion of the Monetary Base by the Federal Reserve not seen since the aftermath of the Crash of 1929, and a swath of financial sector support programs from the Fed and the Treasury, resulting in a spectacular fifty percent retracement rally from the stock market bottom. This is the narcotic that permits the country to not notice that a leg is missing.
2. A comprehensive program of perception management by the government in conjunction with the financial sector to sustain consumer confidence and reduce the chance of further panic. In other words, a web of well-intentioned deceit, subject to abuse.
3. An understandable preoccupation by the individual with the details of breaking news, and a short term focus on particular events, diversions, and controversies, bread and circuses, without a true appreciation of the 'big picture,' in part because of some very effective public relations campaigns and a natural human reluctance to face hard problems.
This is resulting in a remarkable case of cognitive dissonance in which some of the victims of a spectacular man-made calamity are opposing remedies and aid as too costly and impractical, even as they walk around amongst the bleeding carnage.

For those who read the contemporary literature in the early Thirties, this is nothing new. In the early Thirties there was no sense, except for a few notable exceptions, of the magnitude of what had so recently happened. There was the sense of
life goes on which seems almost eerie now to a modern reader. Indeed, Herbert Hoover could dismiss a delegation of concerned citizens with the advice that they were too late, the crisis was past, and all was well. Sound familiar?
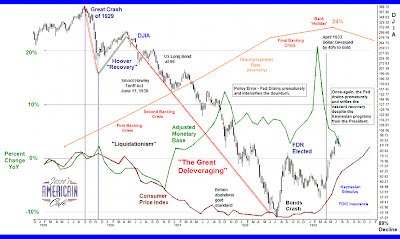
The parallels with the Thirties and the Teens (today) are many, and uncanny.
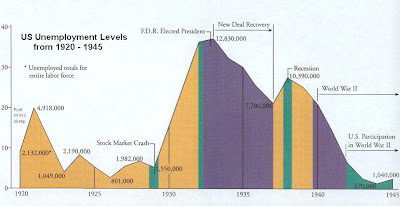
There is the reformer President, elected to redress the extremely pro-business policies of his Republican predecessor. In the Thirties they had FDR who was a decisive and experienced leader. In the Teens the US has a relatively inexperienced community organizer, more influenced by the Wall Street monied interests, and a past history of 'playing safe,' who is trying to manage through indirection and persuasion.
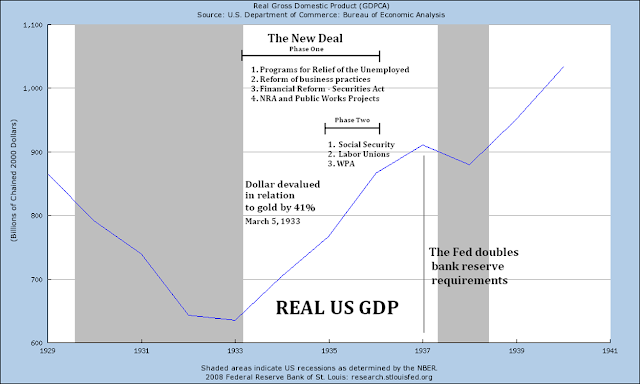
There is a Republican minority in the Congress which opposes all new programs and actions despite giving lip service in order to delay and debilitate. In the Thirties the Republicans were over-ridden by a powerful, activist President, who created a "New Deal" set of legislation, much of which was later overturned by a Supreme Court which had been largely seated by the previous Republican Administrations.
Indeed, the remaining New Deal programs that were successful, the reforms of Glass-Steagall and the safety net of Social Security, are being overturned or are under attack in an almost bucket list fashion.
So what next?
Another leg down in the economy and the financial markets is a high probability.

Although one cannot see it just yet in the fog of corrupted government statistics, the economy is not improving and the US Consumers are flat on their back, scraping by for the most part, except for the upper percentiles who were made fat by the credit bubble, and are still extracting rents from it through officially sanctioned subsidies.
This was no accident; there is a consciousness behind it.
There are far too many otherwise responsible people who are not taking the situation with the high seriousness it deserves. Some would even like to see the US economy collapse, inflicting serious pain and deprivation because it may:
1.suit their investment positions and feed their egos because they think themselves above it all,
2. satisfy their ideological and emotional needs to see punishment administered, almost always to others, for the excesses of the credit bubble, especially if they are relatively weak, unwitting victims, and
3. the sheer nastiness and immaturity of a portion of the population which wallows in stereotypes, childish behaviour, and disappointment with their own lives. They tend to find and follow demagogues that feed their bitter hatreds.
They know not what they do, until they do it, and see the results. It is often a good bet to assume that people will be irrational, almost to the point of idiocy and self-destruction. And some of them never wake up until they are overrun, and then will not admit their error out of a stubborn sense of pride and embarrassment.
It seems likely that there will be a new leg down in financial asset valuations, as reality overcomes often not-so-subtle propaganda and disinformation. It may start in March, or it may be a 'market break' that provides a subtle warning for a large decline that begins in September 2010, with multi year progression to lows that are, as of now, almost unimaginable, at least in real terms. I cannot stress this issue of nominal versus real enough. As inflation comes, it will initially be in a 'stealth' manner, with the backing of the currency eroding slowly but steadily, and largely unrecognized for some time. It is not enough to try and count the dollars; one also has to consider the value behind them, the quality of the wealth, and its vitality. This is the case for stagflation.
The Fed is acting to mask quite a bit of this. One would hope that they would also not re-enact the policy error of their predecessors and raise rates prematurely out of fear of inflation before the structural healing can occur.
The debt incurred during the credit bubble cannot be paid and must be liquidated. So far we have largely seen transference of debt obligations from insiders to the public. Ironically these same insiders are lobbying to maintain these subsidies and transfers, and also to take a hard line against any further remediation of the consequences of the collapse, which they caused, on the public, to have more for themselves. Their greed and hypocrisy know no bounds.
But the policy error might not be caused by the Fed's direct action, but replicated by a governmental failure to stimulate the economy effectively AND to reform the highly inefficient and impractical financial system. The purpose of stimulus is to provide a cushion for structural reform and healing to occur, after an external shock, or even a period of reckless excess and lawlessness. The natural cycle can be disrupted beyond its ability to repair itself. But stimulus without reform is the road to further deterioration and addiction.
As it stands today the global trade system is a farcical construct that favors national elites and multinational corporations. Public policy discussion has been trumped by a handful of economic myths and legends that, even though disproved every day, nevertheless remain resilient in public discussions and reactions. This is because they have become familiar, and because they are the instruments of deception for certain groups of disreputable economists and policy influencers.
A more serious market crash might cause people to recognize the severity of their problems, and the thinness of the arguments of the monied interests for the
status quo which is most clearly unsustainable. But a sizable minority of the population is always highly suggestible; demagogues rely on this.
The eventual outcome for the US is difficult to forecast with any precision now because there are multiple paths that events might take at several key decision points. Some of them might be rather disruptive and upsetting to civil tranquility.
Game changers.
But as the dust continues to settle, the probabilities will continue to clarify.
"Suffering can strengthen our endurance. Endurance encourages strength of character. Character supports hope and confidence even during hard times and trials. And hope does not disappoint us in the end, because God has given us the Spirit and filled our hearts with His love." Romans 5:3-5
It is right to be cautious, and it is human to be afraid. But let us not allow our fears and trials to turn us from our genuine humanity in God's grace no matter how dire the day, even if it may drive some of the world once again into the jaws of desperation and madness. And if you stumble, gather yourself up and go forward again without turning from the way. For what is the profit to gain and hold some small and temporary advantage in this world, but to lose your self, forever.

















.jpg)





































