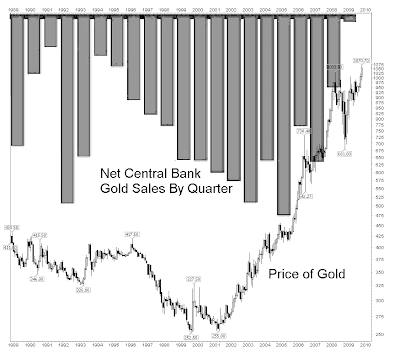
 Starting in 1989, the world's Central Banks became steady net sellers of their gold reserves which had been accumulated over the years.
Starting in 1989, the world's Central Banks became steady net sellers of their gold reserves which had been accumulated over the years.
In addition to official gold sales, the banks also began to engage in gold leasing contract with bullion banks such as J. P. Morgan, Goldman Sachs, et al. The gold was leased, and the bullion bank sells it in the market, paying the lease difference in a sort of gold carry trade.
And now for something completely different, it appears that the world's central banks may once again become net buyers of gold, after a twenty year campaign of selling gold from their vaults into the public markets, creating a steady downward pressure on the price of gold, that contributed to its long bear market.
There is some thought that the central bank gold sales had been designed to support the strong dollar as the reserve currency of the central banks. Gold had been viewed as a threat. Documents which have been disclosed and quotations from the transcripts of central bank meetings do support a concern that the price of gold could rise, destabilizing the fiat regime which had been in place since the US went off the international gold standard in 1971.
Starting in 2001, gold began a bull market based in part by the decline of the US dollar as the undisputed reserve currency of the world. And now the banks are reconsidering their position, and in some cases nervous central bankers seeking to recover their leased bullion, even adding to their reserves by new purchases.
This is not to imply that gold will replace the dollar. Rather, if the intended target is indeed the SDR, which comes up for rebalancing in 2010, banks may need to have gold on hand since it is thought to be favored as a component of the basket of currencies of which the new SDR will be created.
With regard to the proposed IMF sale of 403 tons of gold, there is speculation that this amount may be spoken for already by a few central banks who wish to convert some of their existing US dollar reserves to gold. At a market price of $1,050 per ounce, that would be a total sale of about $13.7 billion. That would barely make a dent in China's dollar reserves should be they so inclined to cut a check.
And of course there are the usual rumours of bullion banks who are heavily 'naked short' gold, having sold the leased product, and are unable to buy physical bullion in size with which to deliver it. There is also some talk of bullion banks having engaged in 'fractional gold' sales to customers holding unallocated bullion. This is cited as one reason why the COMEX in the US has a rule that allows deliver in the futures markets to be made in paper,
Whatever the truth may actually turn out to be, there can be no disputing that an end to twenty years of steady selling of gold, a relatively small and tight market compared to most others, in which central gold reserves represent a significant source of supply, is significant news indeed.
"In its just released Gold Survey 2009 GFMS suggested that the official sector in aggregate became a net buyer in the second quarter of 2009 and forecast that the second half of the year would see further net purchases. This represents a remarkable change of direction for a market that has been used to absorbing substantial volumes of gold sold by central banks over the last decade."GFMS Report
"Over the next year or two this new trend may be obscured somewhat by the planned sales of 403 tonnes of IMF gold, assuming, of course, that there is no off-market transfer of some or all of this bullion to an official sector buyer, something we think improbable but by no means impossible. Once the IMF sales programme is completed, however, we would expect the official sector as a whole to have a broadly neutral impact on the market. This would represent a return to the situation prevailing in the 1970s and 1980s when the official sector was a net buyer in some years and a net seller in others. Besides the obvious supply/demand implications for gold, such a change from net sales to something close to ‘neutrality’ would be highly positive for gold prices, as it ought to provide a major boost to sentiment and confidence in the yellow metal."
“Central banks stand ready to lease gold in increasing quantities should the price rise.” Alan Greenspan, July 24, 1998
A 'fractional reserve' bullion bank would be unnerved by this trend, with visions of potential insolvency if it continues and they are not able to cover their obligations. Talking their book would require them to be quite negative, in the hopes of creating supply in the form of a decent pullback, allowing them to cover their 'short positions' and failed to hedge them adequately.
The biggest forward hedger in the sector, Barrick Gold, was recently forced to capitulate and announce the need to raise billions to buy out of their forward obligations. This still does not help those who are in need of the physical product.
The situation in the silver market is even more potentially explosive, since the CFTC has allowed two or three banks to assume enormous short positions, unprecedented for any other commodity market, amounting to a massive naked short without any conceivable hope of being supplied at today's market prices. But as long as they can keep a few steps ahead of the need to deliver the goods, the game can go on.
A truly remarkable financial system, which can only serve to puzzle future generations. "What were they thinking?"
































